Spectroscopy News
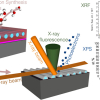
Sequential infiltration synthesis with grazing incidence XRF, XPS and SEM combined with ED X-ray spectroscopy are used for quantification.
Scientists at the Universities of Würzburg and Ottawa have solved the decades-old problem of distinguishing between single and multiple light excitations.
Exploiting dark autoionising states for enhancing extreme ultraviolet laser power relevant for advanced ultrafast science applications such as angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and photoemission electron microscopy.
Multispectral imaging makes it possible to visualise certain functional properties of tissue that are invisible to conventional camera systems, such as the blood perfusion status of an organ.
The combination discerns healthy tissue from tumours based on their spectral profiles with higher accuracy than fluorescence-guided surgery alone.
A new paper has reviewed the combination of instrumentation and computational approaches to coherent Raman scattering.
ACD/Labs will combine their expertise in chemical information management with the knowledge and expertise of ELSIE consortium members to create a searchable knowledge repository of pre-competitive data.
Researchers have pushed the sensitivity of single-atom vibrational spectroscopy to the chemical-bonding-configuration extreme, which is critical for understanding the correlation of lattice vibrational properties with local atomic configurations in materials.
Selective and sensitive measurement of reactive polysulfides in 22 different vegetables using mass spectrometry with a stable-isotope dilution method.
New calibration approach and new NPL reference materials will enable more widespread deployment of proton transfer reaction mass spectrometers (PTR-MS) for long-term atmospheric monitoring.
Researchers at the Fritz Haber Institute have integrated one of the new chiral optical methods with the study of gas-phase anions, which enable mass-selection and the use of a simple table-top laser for observation of the chiral effect.
The new technology integrates several important parts of the spectrometer into one device and is compatible with relatively large magnetic fields.
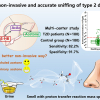
A new non-invasive screening method for T2D uses self-developed proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry.
Acquisition will make electron capture dissociation (ECD) technology available to more biopharma researchers and labs globally.
Pictures from a standard RGB camera combined with AI deep learning can provide equivalent crop prediction tools for a fraction of the cost.
MIDAS helps improve the discovery and characterisation of elusive interactions between proteins and metabolites.
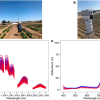
A research team from the USA has used hand-held and tower-based equipment for phenotyping common and tepary beans.
A new method overcomes the resolution-bandwidth limit in chip-scale spectrometry. The proposed scheme is based on a pair of identical tuneable micro-ring resonators.
The new design uses dual-comb spectroscopy.
A new sensor can identify the global content and form of arsenic-containing molecules at very low concentrations.