Spectroscopy News
A technique to combine the ultra-sensitivity of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with a slippery surface invented by researchers at Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, will make it feasible to detect single molecules of a number of chemical and biological species from gaseous, liquid or solid samples.
Electro-optic modulators, which can switch light on and off within just picoseconds, are enabling ever faster telecommunication over fibre optics, and the same tools have now been harnessed for high-speed and accurate molecular sensing in the near infrared.
ChromaDex and American Laboratories have announced the release of a Fourier transform near infrared (FT-NIR) spectroscopy based identification method for the positive identification of desiccated bovine and porcine glandular tissues used in nutritional product formulations.
Photonis USA has announced that it has reached an agreement with MasCom Technologies GmbH of Bremen, Germany, to stock and resell a wide selection of discrete dynode electron multipliers designed for use in inductively coupled mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) instruments. The agreement adds to Photonis’ extensive line of electron multiplier products.
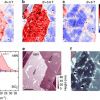
An international group of scientists from Poland, Austria and the UK have used X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy at the UK’s Diamond Light Source to advance our understanding of the changes taking place during the progression of brain cancer. This research may lead the way to a new tumour assessment method which could complement traditional approaches.
A surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) method is to be used to study pesticides on and their penetration into fresh intact produce.
Panorama Synergy Limited has entered into an exclusive global licensing agreement with The University of Western Australia (UWA) for its MEMS-based optical spectroscopy sensor technology.
A newly devised frequency comb provides a powerful light source, spanning frequencies of over 550 GHz with a total power of 5 mW. At the heart of the frequency combs are terahertz (THz) quantum cascade lasers (QCLs), which have the advantage of having both high power (in the form of THz radiation) and broadband capabilities (since the QCLs have gain over a wider frequency range). Combining these two elements to make a compact frequency comb generating long-wavelength light in the THz range can produce a useful source of radiation for a variety of applications in imaging, diagnostics, remote sensing and spectroscopy of extremely complex molecules.
Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis matches bullets to wounds using organ-specific protein signatures found on projectiles.
Panorama Synergy Limited has entered into an exclusive global licensing agreement with The University of Western Australia (UWA) for its MEMS-based optical spectroscopy sensor technology.
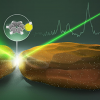
Scientists at EPFL have shown how a light-induced force can amplify the sensitivity and resolution of SERS for the study of single molecules.
A team of researchers has demonstrated a new type of imaging system based on Raman spectroscopy that reveals the chemical composition of living tissue for medical diagnostics and cellular studies.
Horiba Scientific has announced that Francis Ndi, current Export Manager, has been promoted to Product Line Manager for the Optical Spectroscopy Division (OSD).
Oerlikon today announced that it has signed an agreement to sell its Leybold Vacuum business to Atlas Copco. The transaction is based on a valuation of CHF 525 million and is expected to close by middle of the year 2016.
Applied Rigaku Technologies has appointed Koehler Instrument Company as global distributor for the petroleum industry.
Bruker Corporation has appointed Dr Robert Rosenthal to its Board of Directors.
Searching for the precise, complexly folded three-dimensional structure of a protein can be a long, intensive process with uncertain direction. A technique based on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy offers a solution.
Dr Rene Lenggenhager has been appointed President of the Bruker BioSpin Group. He has extensive management experience in international high-tech companies and in the scientific instruments industry.
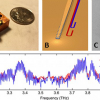
The combination of X-ray structure analysis, infrared spectroscopy and computer simulations has been used to study the switch proteins Ran and Ras with subatomic resolution.
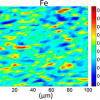
Using Raman spectroscopy and statistical analysis, an international group of scientists has succeeded in taking nanoscale measurements of the strain present at each pixel on the surface of graphene. The researchers also obtained a high-resolution view of the chemical properties of the graphene surface.