Spectroscopy News
A model trained to predict XPS spectra helps researchers to decipher the structure of materials.
ICP-MS of glass tesserae from a villa from late antiquity indicates that some were made from recycled glass, as well as which elements were used for colouring.
Fusion of LIBS and acoustic data to analyse minerals under Terrestrial and Martian atmospheric conditions improves the performance.
Mass spectrometry imaging provides highly precise information on the spatial distribution of substances. Researchers at the University of Bayreuth have succeeded in making visible an additive in dairy products and a production-related contamination in baked goods.
Researchers successfully performed prolonged TERS imaging of µm-scale tungsten disulfide samples without signal degradation
Native ambient mass spectrometry can analyse how drug molecules bind to proteins in tissue samples and could offer an improved route to drug discovery and development.
Researchers at Osaka University have developed a microfluidic system that can measure attomoles of solutes in pL of liquids using terahertz radiation.
THe first transmission spectrum made from a single observation using Webb’s Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) reveals atmospheric characteristics of the hot gas giant exoplanet WASP-96 b.
Ultrasensitive biosensors based on SERS have been developed to detect the cancer metastasis related programmed death ligand (PD-L1) biomarker.
Researchers have created an ultrathin SERS sensor, spun from gold, that can be attached directly to the skin without irritation or discomfort.
An NMR-based Molecular Phenomics Clinical Research Tool for “Long COVID” multi-organ risk assessment uses a multiplexed combination of biomarkers.
Headwall Photonics has acquired perClass BV, the developer of the perClass Mira® spectral analysis software package.
Using a new method, helical dichroism in the X-ray domain, scientists are better able to distinguish between chiral substances.
Researchers are developing technology for compact high-performance magnetic resonance units, 200× smaller than current systems.
Raman spectra of battery electrolytes provide unique information on their chemical state-of-health.
A Chinese team has developed a new algorithm for near infrared spectroscopy, suitable for high-throughput identification of the authenticity of crop varieties.
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba are using ultrafast spectroscopy to measure tiny changes in magnetic fields using nitrogen-vacancy defects in diamonds, paving the way for more accurate quantum sensors for spintronic computers.
Infrared and Raman spectroscopy have been used to identify lysine acetylation features, which provided a theoretical and experimental basis for the analysis of protein acetylation structures in biological systems.
An international team of researchers has demonstrated attosecond-pump attosecond-probe spectroscopy to study non-linear multi-photon ionisation of atoms.



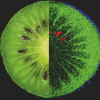
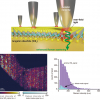
![Targeted proton transfer charge reduction (tPTCR) nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging of liver tissue from orally dosed rat (Animal 3). a) optical image of a blood vessel within liver tissue. b) Composite ion image of charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2259.9 and m/z 2636.3 respectively, red) and the charged-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2097.5 and m/z 2446.9 respectively, blue). c) Ion image composed from charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in blood vessels. d) Ion image composed from charge-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in bulk tissue and absence in the blood vessel. Reproduced from https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202202075 under a CC BY licence. Light and mass spectromert imaging of tissue samples](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail/public/news/MSI%20drug-protein%20complex-w.jpg?itok=CBNIjyYl)